F-shape barrier
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2010) |
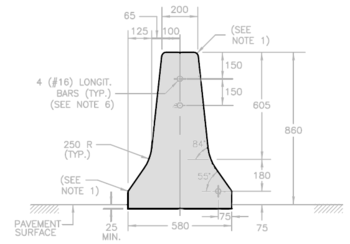
The F-shape barrier is a concrete crash barrier, originally designed to divide lanes of traffic on a highway. It is a modification of the widely used Jersey barrier design, and is generally considered safer.[1]
A parametric study, one that systematically varies the parameters, was done through computer simulations of barrier profiles labeled A through F. The result showed that the one labeled F performed better than even the shape of the Jersey barrier. A series of full-scale crash tests later confirmed these computer-based results. What is known today as the F-shape barrier takes its name from the label it was given on these tests and not from any part of the shape of the barrier, unlike, for example, T-walls.
In spite of these tests, the F-shape barrier has not supplanted the Jersey-shape. The Jersey-shape barrier was already in wide use, and it also met the crash-test criteria. The states' contractors already had a significant investment in the Jersey-shape casting forms and it would cost them money to change the profiles of the forms.
The F-shape and the Jersey-shape have the same slopes, but the distance from the ground to the slope break point of the F-shape is 255 millimetres (10.0 in), which is 75 millimetres (3.0 in) lower than the Jersey-shape. This lower slope break point reduces vehicle lift, improving the barrier's performance.
Because the Jersey-shape design requires very little modification to become an F-shape design, asphalt resurfacing, because it raises the overall height of the road surface relative to the barrier, can convert the Jersey-shape barrier into a more F-shape-like barrier that is safer for lighter cars. However, these increased layers of asphalt also reduce the working height of the barrier which reduces its effectiveness for heavier vehicles.
The UK equivalent is the concrete step barrier.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Basics of Concrete Barriers". Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center. Archived from the original on 2006-04-27. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
