Poitevin–Saintongeais
| Poitevin–Saintongeais | |
|---|---|
| poetevin–séntunjhaes | |
| Native to | France |
| Region | Pays de la Loire Nouvelle-Aquitaine |
Native speakers | 200,000–300,000 (2017)[1] |
Early forms | |
| Dialects | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | poit1240 Poitevinsant1407 Santongeais |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-ha |
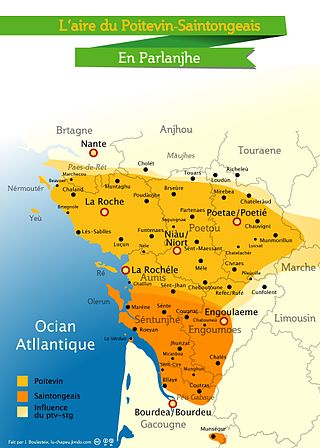 The Poitevin-Saintongeais-speaking area | |

Poitevin–Saintongeais (French: poitevin–saintongeais, pronounced [pwatvɛ̃ sɛ̃tɔ̃ʒɛ]; Poitevin–Saintongeais: poetevin-séntunjhaes;[3] also called Parlanjhe, Aguiain or Aguiainais in French) is a language spoken in the regions of the Pays de la Loire and Nouvelle-Aquitaine. Poitevin–Saintongeais is officially recognised by the French Ministry of Culture as a language with two dialects: Poitevin and Saintongeais.[4] The language belongs to the langues d'oïl subbranch of the Gallo-Romance languages.
Some descendants of Poitevin–Saintongeais speakers became the Acadian people of Atlantic Canada as well as the Cajun people of Louisiana.[citation needed]
The dialects of this language are peculiar to the historical regions and provinces of Poitou and Saintonge. It is classified as severely endangered by UNESCO.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ Delavaud, Jean (4 March 2017). "Langues régionales. Une journée pour parler le poitevin-saintongeais" [Regional languages. A day to speak Poitevin-Saintongeais]. Ouest-France (in French). Archived from the original on 26 September 2021. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (24 May 2022). "Oil". Glottolog. Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. Archived from the original on 8 October 2022. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ^ Produccions, Tirabol (13 August 2012). "Lo peitavin-santongés, una lenga sòrre e emergenta". Jornalet (in Occitan). Archived from the original on 5 September 2017. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ "Langues régionales" (in French). Ministère de la Culture. Archived from the original on 1 April 2018. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ "UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in danger". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
