Portal:Medicine
The Medicine Portal

Medicine is the refined science and disciplined practice of tending to patients, encompassing the comprehensive management of diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, and treatment of their injuries or ailments, as well as the promotion of overall health and well-being. This field spans a diverse range of healthcare practices that have evolved over centuries, all with the objective of preserving and restoring health through the prevention and alleviation of illness.
Modern medicine draws extensively upon biomedical sciences, cutting-edge research, genetics, and advanced medical technologies to accurately diagnose, treat, and prevent disease and injury. Traditional approaches, such as pharmaceuticals and surgical intervention, are central to contemporary treatment; however, a wide array of therapies are also employed, including psychotherapy, external supports like splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, among others. These varied methods form the foundation of medicine’s commitment to comprehensive care and innovation.
Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of creativity and skill), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancient philosopher and physician would apply bloodletting according to the theories of humorism. In recent centuries, since the advent of modern science, most medicine has become a combination of art and science (both basic and applied, under the umbrella of medical science). For example, while stitching technique for sutures is an art learned through practice, knowledge of what happens at the cellular and molecular level in the tissues being stitched arises through science. (Full article...)
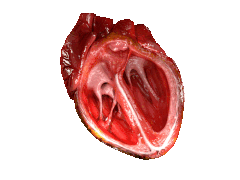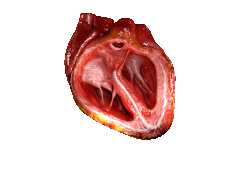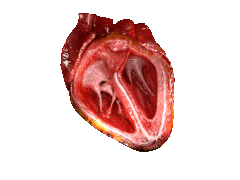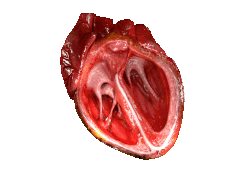
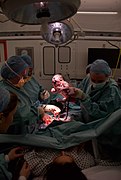
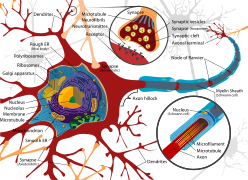
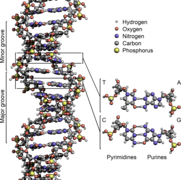
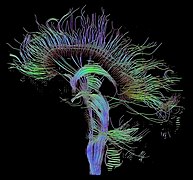
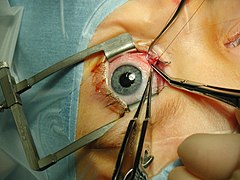
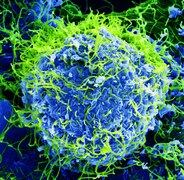
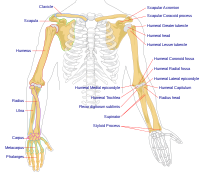
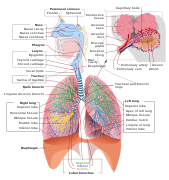
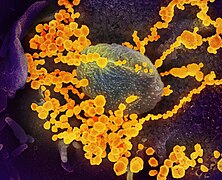
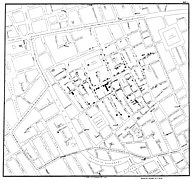
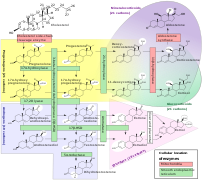
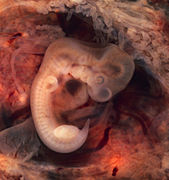
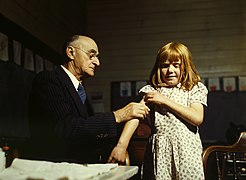
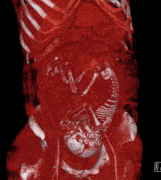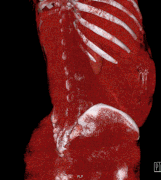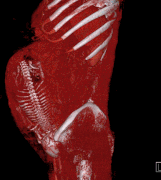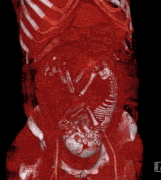
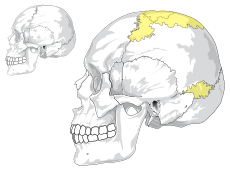
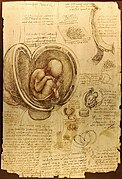
Selected image –
WikiProject

Get involved by joining WikiProject Medicine. We discuss collaborations and all manner of issues on our talk page.
Related portals
Did you know –
- ...Peyer's patches are an example of gut-associated lymphoid tissue?
- ...the brain itself is not sensitive to pain, because it lacks pain-sensitive nerve fibers? Several areas of the head can hurt, including a network of nerves which extends over the scalp and certain nerves in the face, mouth, and throat.
- ...that irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) may sometimes have an acute onset and develop after an infectious illness, and that this "Post infectious IBS" (IBS-PI) is drawing much clinical investigation?
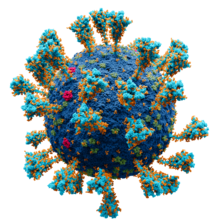
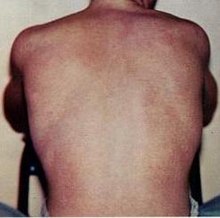
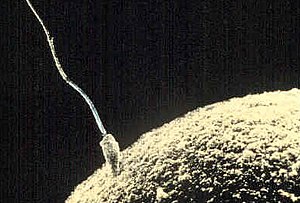
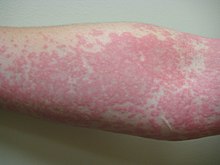
General images –
More Did you know (auto generated)

- ... that fourteenth-century Buddhist monk Tuệ Tĩnh is referred to as a founding father of traditional Vietnamese medicine?
- ... that Tang Zonghai was one of the first advocates for the integration of Chinese and Western medicine?
- ... that a lack of screening for pregnant women with syphilis in sub-Saharan Africa is associated with increased infant mortality?
- ... that the Noongar used the Eucalyptus wandoo tree as a medicine and ointment?
- ... that Constance Fozzard was told during her surgical training that women with children could not become consultants?
- ... that the Anglo-Saxons may have used a mixture of garlic, another Allium, wine, and bovine bile as an eye medicine?
Topics
Categories
Recognized content
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus

![Image 1 Anti-FGM road sign near Kapchorwa, Uganda, 2004 Female genital mutilation (FGM) (also known as female genital cutting, female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) and female circumcision) is the cutting or removal of some or all of the vulva for non-medical reasons. FGM prevalence varies worldwide, but is majorly present in some countries of Africa, Asia and Middle East, and within their diasporas. As of 2024[update], UNICEF estimates that worldwide 230 million girls and women (144 million in Africa, 80 million in Asia, 6 million in Middle East, and 1-2 million in other parts of the world) had been subjected to one or more types of FGM. Typically carried out by a traditional circumciser using a blade, FGM is conducted from days after birth to puberty and beyond. In half of the countries for which national statistics are available, most girls are cut before the age of five. Procedures differ according to the country or ethnic group. They include removal of the clitoral hood (type 1-a) and clitoral glans (1-b); removal of the inner labia (2-a); and removal of the inner and outer labia and closure of the vulva (type 3). In this last procedure, known as infibulation, a small hole is left for the passage of urine and menstrual fluid, the vagina is opened for intercourse and opened further for childbirth. (Full article...)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png)












































![Image 25Global concentrations of health care resources, as depicted by the number of physicians per 10,000 individuals, by country. Data is sourced from a World Health Statistics 2010, a WHO report.[needs update] (from Health care)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1f/Global_physician_density_map_-_WHO_2010.png/120px-Global_physician_density_map_-_WHO_2010.png)